Secure University College Network System Design and Implementation
Scenario Description: Secure Campus Network:
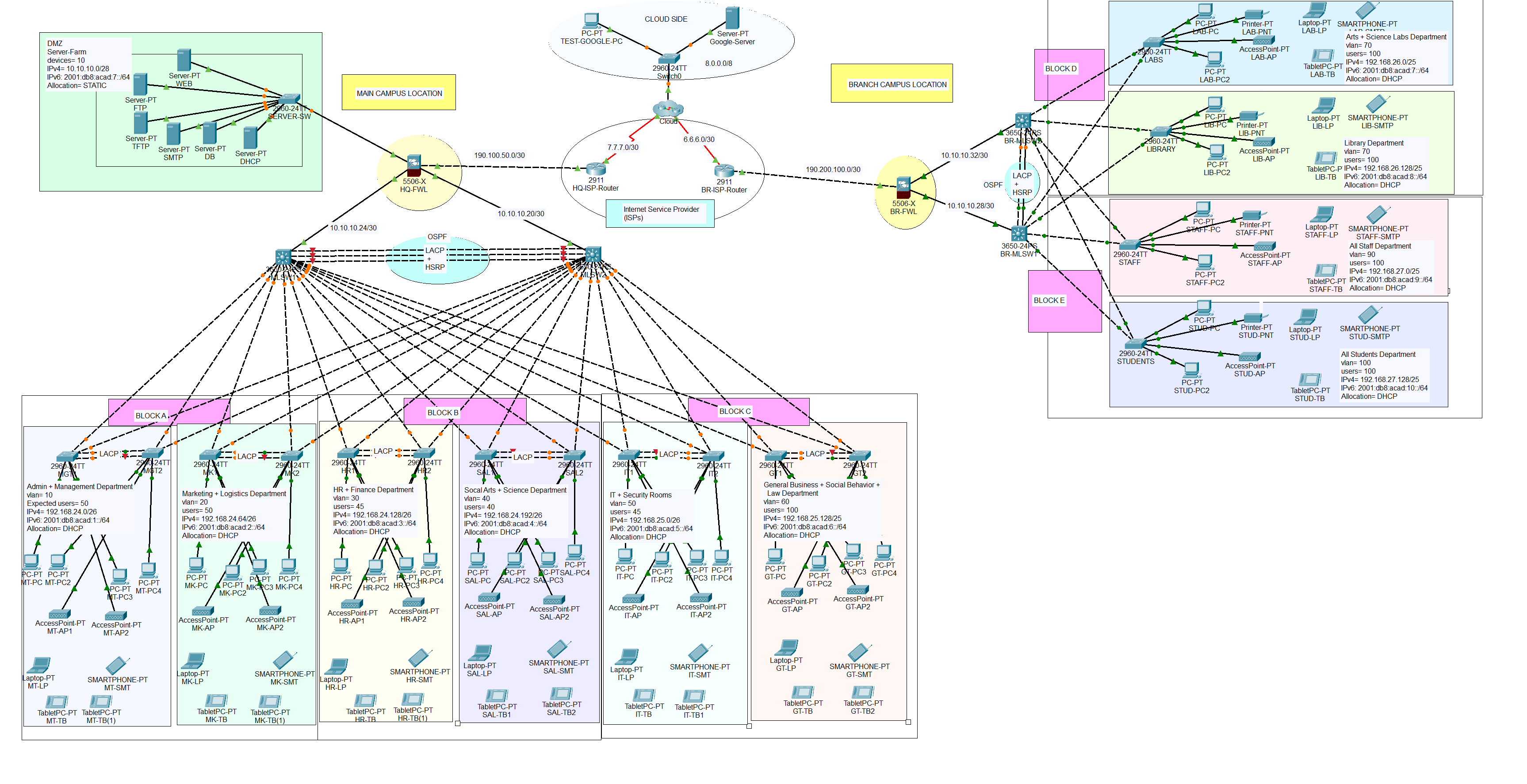
ABC Corp operates with two main campuses: the Main Campus and the Branch Campus, each designed to support a collaborative and secure network environment. The Main Campus houses six departments alongside a centralized server farm that serves both campuses, ensuring efficient resource sharing and data access. The Branch Campus consists of four departments and is designed to interconnect seamlessly with the Main Campus while maintaining a robust security posture. Both campuses prioritize high availability and employ strategic segmentation and redundancy to enhance reliability and scalability.
To secure and manage network traffic, each campus connects to its local ISP through a Cisco ASA firewall that inspects incoming and outgoing traffic, providing a crucial layer of security against external threats. The network design integrates redundant core and distribution switches at each campus to maintain continuous service, even in the event of hardware failure. VLANs are implemented to segment departmental traffic, ensuring secure communication within and between campuses while minimizing potential broadcast domains and isolating sensitive data.
Scalability is built into the network by designing with future growth in mind, enabling the addition of new departments or devices without major overhauls. The use of dynamic routing protocols like OSPF supports efficient route sharing and fast convergence, enhancing the network’s adaptability and performance. The server farm at the Main Campus is secured through access control lists (ACLs) and strict policies, with the Cisco ASA firewall providing an additional inspection layer, ensuring all connections between the campuses are encrypted and secure, meeting the company’s high standards for redundancy, scalability, and security.
- All Device Basic Configurations: Standard initial setup and security configurations for all network devices.
- VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks): Network segmentation for better traffic management and security.
- Inter-VLAN Routing: Facilitating communication between different VLANs.
- EtherChannel: Link aggregation for increased bandwidth and redundancy between switches.
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First): Dynamic routing protocol for efficient route management and quick convergence.
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Automated IP address allocation across the network.
- Other Servers: Implementation of additional services, such as DNS and WEB servers.
- HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol): Ensuring high availability and redundancy for gateway devices.
- SSH (Secure Shell): Secure remote access to network devices.
- ACLs (Access Control Lists): Traffic filtering to control and secure network access.
- WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network): Wireless connectivity for end users with secure access points.
- NAT (Network Address Translation): Facilitating secure communication between internal and external networks.
- Firewalls with Inspection Policies: Enhanced traffic inspection and threat mitigation at network perimeters.
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone): Isolated area for hosting public-facing services.
- ISP Routers: Configuration of routers connecting the campus to internet service providers.
- Internet Servers: Setup for web hosting and external service applications.
The network topology below satisfy the user requirements above and everything is verified, tested and working fine.